RabbitMQ整理-基础篇
1.前言
1.1.几种常见的消息队列
消息Broker,目前常见的实现方案就是消息队列(MessageQueue),简称为MQ. 目比较常见的MQ实现:
ActiveMQ
RabbitMQ
RocketMQ
Kafka
几种常见MQ的对比:
RabbitMQ | ActiveMQ | RocketMQ | Kafka | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
公司/社区 | Rabbit | Apache | 阿里 | Apache |
开发语言 | Erlang | Java | Java | Scala&Java |
协议支持 | AMQP,XMPP,SMTP,STOMP | OpenWire,STOMP,REST,XMPP,AMQP | 自定义协议 | 自定义协议 |
可用性 | 高 | 一般 | 高 | 高 |
单机吞吐量 | 一般 | 差 | 高 | 非常高 |
消息延迟 | 微秒级 | 毫秒级 | 毫秒级 | 毫秒以内 |
消息可靠性 | 高 | 一般 | 高 | 一般 |
追求可用性:Kafka、 RocketMQ 、RabbitMQ 追求可靠性:RabbitMQ、RocketMQ 追求吞吐能力:RocketMQ、Kafka 追求消息低延迟:RabbitMQ、Kafka
据统计,目前国内消息队列使用最多的还是RabbitMQ,再加上其各方面都比较均衡,稳定性也好。
2.RabbitMQ
RabbitMQ是基于Erlang语言开发的开源消息通信中间件,官网地址: Messaging that just works — RabbitMQ
2.1.安装
基于Docker来安装RabbitMQ,使用下面的命令即可:
docker run \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_USER=itheima \
-e RABBITMQ_DEFAULT_PASS=123321 \
-v mq-plugins:/plugins \
--name mq \
--hostname mq \
-p 15672:15672 \
-p 5672:5672 \
--network hmall \
-d \
rabbitmq:3.8-management可以看到在安装命令中有两个映射的端口:
15672:RabbitMQ提供的管理控制台的端口
5672:RabbitMQ的消息发送处理接口
安装完成后,访问 http://192.168.150.101:15672即可看到管理控制台。首次访问需要登录,默认的用户名和密码在配置文件中已经指定了。 登录后即可看到管理控制台总览页面:

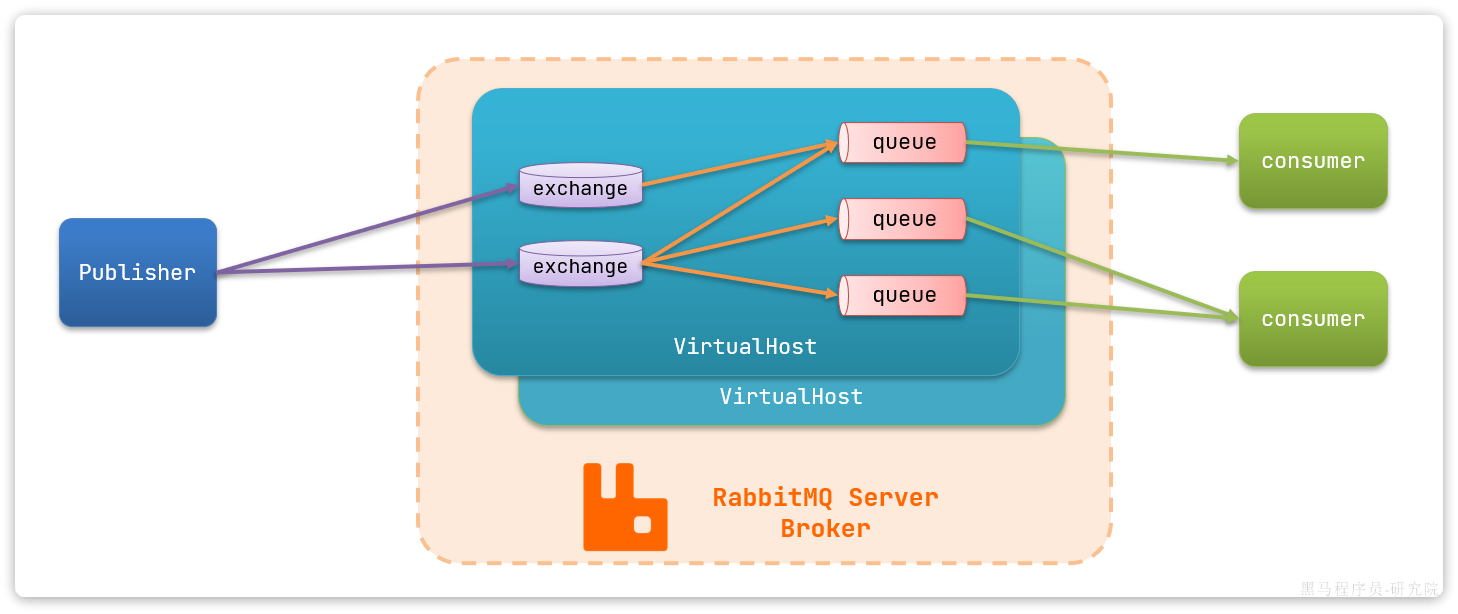
RabbitMQ对应的架构如图:

其中包含几个概念:
publisher:生产者,也就是发送消息的一方consumer:消费者,也就是消费消息的一方queue:队列,存储消息。生产者投递的消息会暂存在消息队列中,等待消费者处理exchange:交换机,负责消息路由。生产者发送的消息由交换机决定投递到哪个队列。virtual host:虚拟主机,起到数据隔离的作用。每个虚拟主机相互独立,有各自的exchange、queue
上述这些东西都可以在RabbitMQ的管理控制台来管理。
2.2.收发消息
2.2.1.交换机
打开Exchanges选项卡,可以看到已经存在很多交换机:
点击任意交换机,即可进入交换机详情页面。仍然会利用控制台中的publish message 发送一条消息:

这里是由控制台模拟了生产者发送的消息。由于没有消费者存在,最终消息丢失了,这样说明交换机没有存储消息的能力。
2.2.2.队列
打开Queues选项卡,新建一个队列:
命名为hello.queue1:

再以相同的方式,创建一个队列,密码为hello.queue2,最终队列列表如下:

此时,再次向amq.fanout交换机发送一条消息。会发现消息依然没有到达队列!! 怎么回事呢? 发送到交换机的消息,只会路由到与其绑定的队列,因此仅仅创建队列是不够的,还需要将其与交换机绑定。
2.2.3.绑定关系
点击Exchanges选项卡,点击amq.fanout交换机,进入交换机详情页,然后点击Bindings菜单,在表单中填写要绑定的队列名称:

相同的方式,将hello.queue2也绑定到改交换机。
2.2.4.发送消息
再次回到exchange页面,找到刚刚绑定的amq.fanout,点击进入详情页,再次发送一条消息:
 回到
回到Queues页面,可以发现hello.queue中已经有一条消息了:

 点击队列名称,进入详情页,查看队列详情,这次我们点击get message:
点击队列名称,进入详情页,查看队列详情,这次我们点击get message:
 可以看到消息到达队列了:
可以看到消息到达队列了:

 这个时候如果有消费者监听了MQ的
这个时候如果有消费者监听了MQ的hello.queue1或hello.queue2队列,自然就能接收到消息了。
2.3.数据隔离
2.3.1.用户管理
点击Admin选项卡,首先会看到RabbitMQ控制台的用户管理界面:

 这里的用户都是RabbitMQ的管理或运维人员。目前只有安装RabbitMQ时添加的
这里的用户都是RabbitMQ的管理或运维人员。目前只有安装RabbitMQ时添加的itheima这个用户。仔细观察用户表格中的字段,如下:
Name:itheima,也就是用户名Tags:administrator,说明itheima用户是超级管理员,拥有所有权限Can access virtual host:/,可以访问的virtual host,这里的/是默认的virtual host
对于小型企业而言,出于成本考虑,我们通常只会搭建一套MQ集群,公司内的多个不同项目同时使用。这个时候为了避免互相干扰, 我们会利用virtual host的隔离特性,将不同项目隔离。一般会做两件事情:
给每个项目创建独立的运维账号,将管理权限分离。
给每个项目创建不同的
virtual host,将每个项目的数据隔离。
比如,我们给黑马商城创建一个新的用户,命名为hmall:

 你会发现此时hmall用户没有任何
你会发现此时hmall用户没有任何virtual host的访问权限:
 别急,接下来我们就来授权。
别急,接下来我们就来授权。
2.3.2.virtual host
我们先退出登录:
 切换到刚刚创建的hmall用户登录,然后点击
切换到刚刚创建的hmall用户登录,然后点击Virtual Hosts菜单,进入virtual host管理页:
 可以看到目前只有一个默认的
可以看到目前只有一个默认的virtual host,名字为 /。 我们可以给黑马商城项目创建一个单独的virtual host,而不是使用默认的/。

 创建完成后如图:
创建完成后如图:

 由于我们是登录
由于我们是登录hmall账户后创建的virtual host,因此回到users菜单,你会发现当前用户已经具备了对/hmall这个virtual host的访问权限了:
此时,点击页面右上角的virtual host下拉菜单,切换virtual host为 /hmall:

 然后再次查看queues选项卡,会发现之前的队列已经看不到了
然后再次查看queues选项卡,会发现之前的队列已经看不到了
 这就是基于
这就是基于virtual host的隔离效果。
3.SpringAMQP
将来我们开发业务功能的时候,肯定不会在控制台收发消息,而是应该基于编程的方式。由于RabbitMQ采用了AMQP协议,因此它具备跨语言的特性。任何语言只要遵循AMQP协议收发消息,都可以与RabbitMQ交互。并且RabbitMQ官方也提供了各种不同语言的客户端。 但是,RabbitMQ官方提供的Java客户端编码相对复杂,一般生产环境下我们更多会结合Spring来使用。而Spring的官方刚好基于RabbitMQ提供了这样一套消息收发的模板工具:SpringAMQP。并且还基于SpringBoot对其实现了自动装配,使用起来非常方便。
SpringAmqp的官方地址: Spring AMQP SpringAMQP提供了三个功能:
自动声明队列、交换机及其绑定关系
基于注解的监听器模式,异步接收消息
封装了RabbitTemplate工具,用于发送消息
这一章我们就一起学习一下,如何利用SpringAMQP实现对RabbitMQ的消息收发。
3.1.Demo工程
项目结构如图:

 包括三部分:
包括三部分:
mq-demo:父工程,管理项目依赖
publisher:消息的发送者
consumer:消息的消费者
在mq-demo这个父工程中,已经配置好了SpringAMQP相关的依赖:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>cn.itcast.demo</groupId>
<artifactId>mq-demo</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<modules>
<module>publisher</module>
<module>consumer</module>
</modules>
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.7.12</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>8</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>8</maven.compiler.target>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--AMQP依赖,包含RabbitMQ-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!--单元测试-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</project>因此,子工程中就可以直接使用SpringAMQP了。
3.2.快速入门
在之前的案例中,我们都是经过交换机发送消息到队列,不过有时候为了测试方便,我们也可以直接向队列发送消息,跳过交换机。 在入门案例中,我们就演示这样的简单模型,如图:

 也就是:
也就是:
publisher直接发送消息到队列
消费者监听并处理队列中的消息
warning 注意:这种模式一般测试使用,很少在生产中使用。
为了方便测试,我们现在控制台新建一个队列:simple.queue

 接下来,我们就可以利用Java代码收发消息了。
接下来,我们就可以利用Java代码收发消息了。
3.1.1.消息发送
首先配置MQ地址,在publisher服务的application.yml中添加配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.150.101 # 你的虚拟机IP
port: 5672 # 端口
virtual-host: /hmall # 虚拟主机
username: hmall # 用户名
password: 123 # 密码然后在publisher服务中编写测试类SpringAmqpTest,并利用RabbitTemplate实现消息发送:
package com.itheima.publisher.amqp;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
public class SpringAmqpTest {
@Autowired
private RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate;
@Test
public void testSimpleQueue() {
// 队列名称
String queueName = "simple.queue";
// 消息
String message = "hello, spring amqp!";
// 发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, message);
}
}打开控制台,可以看到消息已经发送到队列中:

 接下来,我们再来实现消息接收。
接下来,我们再来实现消息接收。
3.1.2.消息接收
首先配置MQ地址,在consumer服务的application.yml中添加配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
host: 192.168.150.101 # 你的虚拟机IP
port: 5672 # 端口
virtual-host: /hmall # 虚拟主机
username: hmall # 用户名
password: 123 # 密码然后在consumer服务的com.itheima.consumer.listener包中新建一个类SpringRabbitListener,代码如下:
package com.itheima.consumer.listener;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class SpringRabbitListener {
// 利用RabbitListener来声明要监听的队列信息
// 将来一旦监听的队列中有了消息,就会推送给当前服务,调用当前方法,处理消息。
// 可以看到方法体中接收的就是消息体的内容
@RabbitListener(queues = "simple.queue")
public void listenSimpleQueueMessage(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("spring 消费者接收到消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
}3.1.3.测试
启动consumer服务,然后在publisher服务中运行测试代码,发送MQ消息。最终consumer收到消息:

3.3.WorkQueues模型
Work queues,任务模型。简单来说就是让多个消费者绑定到一个队列,共同消费队列中的消息。
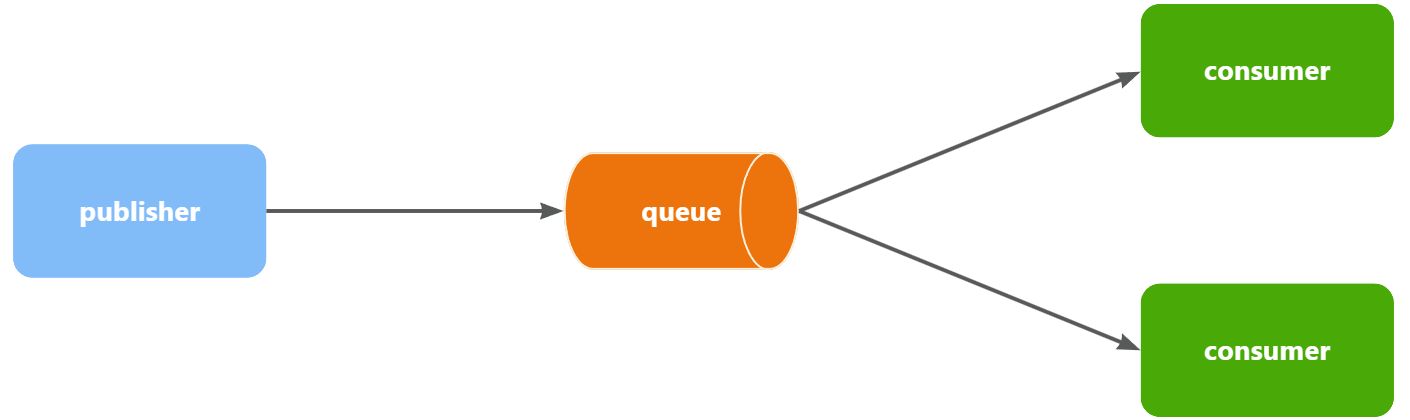

当消息处理比较耗时的时候,可能生产消息的速度会远远大于消息的消费速度。长此以往,消息就会堆积越来越多,无法及时处理。 此时就可以使用work 模型,多个消费者共同处理消息处理,消息处理的速度就能大大提高了。
接下来,我们就来模拟这样的场景。 首先,我们在控制台创建一个新的队列,命名为work.queue:


3.3.1.消息发送
这次我们循环发送,模拟大量消息堆积现象。 在publisher服务中的SpringAmqpTest类中添加一个测试方法:
/**
* workQueue
* 向队列中不停发送消息,模拟消息堆积。
*/
@Test
public void testWorkQueue() throws InterruptedException {
// 队列名称
String queueName = "simple.queue";
// 消息
String message = "hello, message_";
for (int i = 0; i < 50; i++) {
// 发送消息,每20毫秒发送一次,相当于每秒发送50条消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(queueName, message + i);
Thread.sleep(20);
}
}3.3.2.消息接收
要模拟多个消费者绑定同一个队列,我们在consumer服务的SpringRabbitListener中添加2个新的方法:
@RabbitListener(queues = "work.queue")
public void listenWorkQueue1(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到消息:【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
Thread.sleep(20);
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "work.queue")
public void listenWorkQueue2(String msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.err.println("消费者2........接收到消息:【" + msg + "】" + LocalTime.now());
Thread.sleep(200);
}注意到这两消费者,都设置了Thead.sleep,模拟任务耗时:
消费者1 sleep了20毫秒,相当于每秒钟处理50个消息
消费者2 sleep了200毫秒,相当于每秒处理5个消息
3.3.3.测试
启动ConsumerApplication后,在执行publisher服务中刚刚编写的发送测试方法testWorkQueue。 最终结果如下:
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_0】21:06:00.869555300
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_1】21:06:00.884518
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_2】21:06:00.907454400
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_4】21:06:00.953332100
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_6】21:06:00.997867300
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_8】21:06:01.042178700
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_3】21:06:01.086478800
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_10】21:06:01.087476600
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_12】21:06:01.132578300
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_14】21:06:01.175851200
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_16】21:06:01.218533400
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_18】21:06:01.261322900
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_5】21:06:01.287003700
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_20】21:06:01.304412400
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_22】21:06:01.349950100
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_24】21:06:01.394533900
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_26】21:06:01.439876500
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_28】21:06:01.482937800
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_7】21:06:01.488977100
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_30】21:06:01.526409300
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_32】21:06:01.572148
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_34】21:06:01.618264800
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_36】21:06:01.660780600
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_9】21:06:01.689189300
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_38】21:06:01.705261
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_40】21:06:01.746927300
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_42】21:06:01.789835
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_44】21:06:01.834393100
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_46】21:06:01.875312100
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_11】21:06:01.889969500
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_48】21:06:01.920702500
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_13】21:06:02.090725900
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_15】21:06:02.293060600
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_17】21:06:02.493748
...省略
可以看到消费者1和消费者2竟然每人消费了25条消息:
消费者1很快完成了自己的25条消息
消费者2却在缓慢的处理自己的25条消息。
也就是说消息是平均分配给每个消费者,并没有考虑到消费者的处理能力。导致1个消费者空闲,另一个消费者忙的不可开交。没有充分利用每一个消费者的能力,最终消息处理的耗时远远超过了1秒。这样显然是有问题的。
3.3.4.能者多劳
在spring中有一个简单的配置,可以解决这个问题。我们修改consumer服务的application.yml文件,添加配置:
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
prefetch: 1 # 每次只能获取一条消息,处理完成才能获取下一个消息再次测试,发现结果如下:
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_0】21:12:51.659664200
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_1】21:12:51.680610
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_2】21:12:51.703625
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_3】21:12:51.724330100
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_4】21:12:51.746651100
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_5】21:12:51.768401400
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_6】21:12:51.790511400
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_7】21:12:51.812559800
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_8】21:12:51.834500600
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_9】21:12:51.857438800
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_10】21:12:51.880379600
消费者2........接收到消息:【hello, message_11】21:12:51.899327100
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_12】21:12:51.922828400
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_13】21:12:51.945617400
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_14】21:12:51.968942500
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_15】21:12:51.992215400
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_16】21:12:52.013325600
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_17】21:12:52.035687100
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_18】21:12:52.058188
消费者1接收到消息:【hello, message_19】21:12:52.081208400
...省略
可以发现,由于消费者1处理速度较快,所以处理了更多的消息;消费者2处理速度较慢,只处理了6条消息。而最终总的执行耗时也在1秒左右,大大提升。 正所谓能者多劳,这样充分利用了每一个消费者的处理能力,可以有效避免消息积压问题。
3.3.5.总结
Work模型的使用:
多个消费者绑定到一个队列,同一条消息只会被一个消费者处理
通过设置prefetch来控制消费者预取的消息数量
3.4.交换机类型
在之前的两个测试案例中,都没有交换机,生产者直接发送消息到队列。而一旦引入交换机,消息发送的模式会有很大变化:

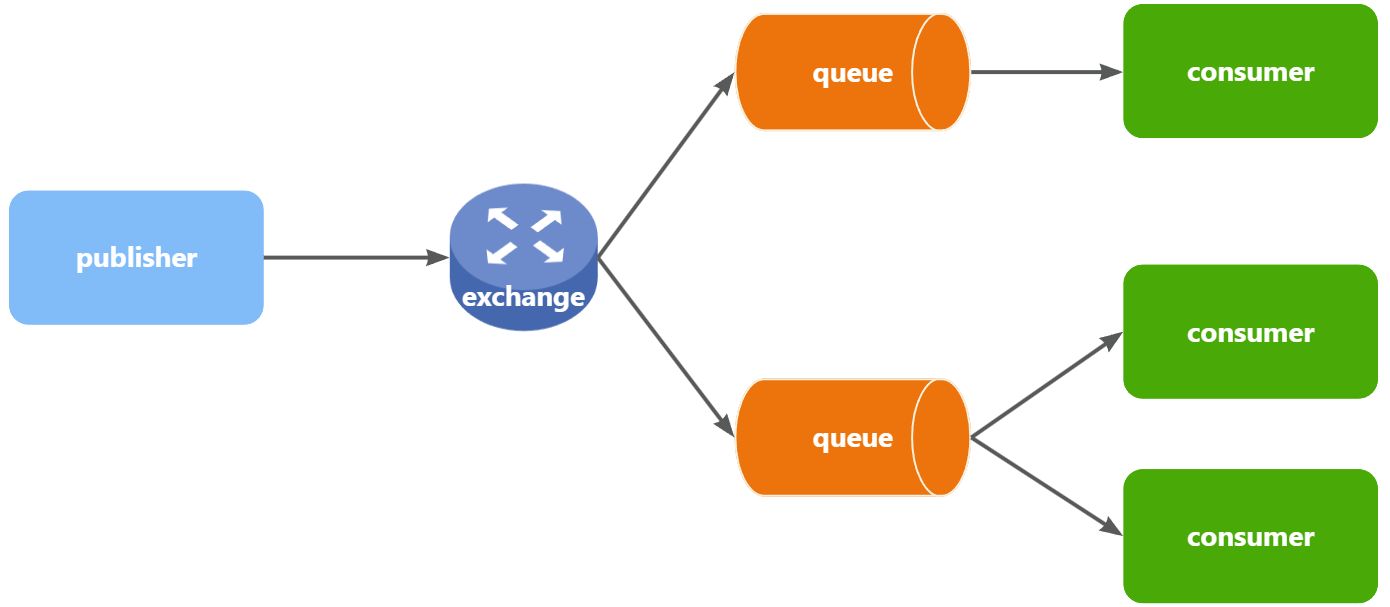 可以看到,在订阅模型中,多了一个exchange角色,而且过程略有变化:
可以看到,在订阅模型中,多了一个exchange角色,而且过程略有变化:
Publisher:生产者,不再发送消息到队列中,而是发给交换机
Exchange:交换机,一方面,接收生产者发送的消息。另一方面,知道如何处理消息,例如递交给某个特别队列、递交给所有队列、或是将消息丢弃。到底如何操作,取决于Exchange的类型。
Queue:消息队列也与以前一样,接收消息、缓存消息。不过队列一定要与交换机绑定。
Consumer:消费者,与以前一样,订阅队列,没有变化
Exchange(交换机)只负责转发消息,不具备存储消息的能力,因此如果没有任何队列与Exchange绑定,或者没有符合路由规则的队列,那么消息会丢失!
交换机的类型有四种:
Fanout:广播,将消息交给所有绑定到交换机的队列。我们最早在控制台使用的正是Fanout交换机
Direct:订阅,基于RoutingKey(路由key)发送给订阅了消息的队列
Topic:通配符订阅,与Direct类似,只不过RoutingKey可以使用通配符
Headers:头匹配,基于MQ的消息头匹配,用的较少。
课堂中,我们讲解前面的三种交换机模式。
3.5.Fanout交换机
Fanout,英文翻译是扇出,我觉得在MQ中叫广播更合适。 在广播模式下,消息发送流程是这样的:


1) 可以有多个队列
2) 每个队列都要绑定到Exchange(交换机)
3) 生产者发送的消息,只能发送到交换机
4) 交换机把消息发送给绑定过的所有队列
5) 订阅队列的消费者都能拿到消息
我们的计划是这样的:


创建一个名为
hmall.fanout的交换机,类型是Fanout创建两个队列
fanout.queue1和fanout.queue2,绑定到交换机hmall.fanout
3.5.1.声明队列和交换机
在控制台创建队列fanout.queue1:

 同样再创建一个队列
同样再创建一个队列fanout.queue2:
 然后再创建一个交换机:
然后再创建一个交换机:

 然后绑定两个队列到交换机:
然后绑定两个队列到交换机:

 3.5.2.消息发送
3.5.2.消息发送
在publisher服务的SpringAmqpTest类中添加测试方法:
@Test
public void testFanoutExchange() {
// 交换机名称
String exchangeName = "hmall.fanout";
// 消息
String message = "hello, everyone!";
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "", message);
}3.5.3.消息接收
在consumer服务的SpringRabbitListener中添加两个方法,作为消费者:
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue1")
public void listenFanoutQueue1(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到Fanout消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "fanout.queue2")
public void listenFanoutQueue2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到Fanout消息:【" + msg + "】");
}3.5.4.总结
交换机的作用是什么?
接收publisher发送的消息
将消息按照规则路由到与之绑定的队列
不能缓存消息,路由失败,消息丢失
FanoutExchange的会将消息路由到每个绑定的队列
3.6.Direct交换机
在Fanout模式中,一条消息,会被所有订阅的队列都消费。但是,在某些场景下,我们希望不同的消息被不同的队列消费。这时就要用到Direct类型的Exchange。
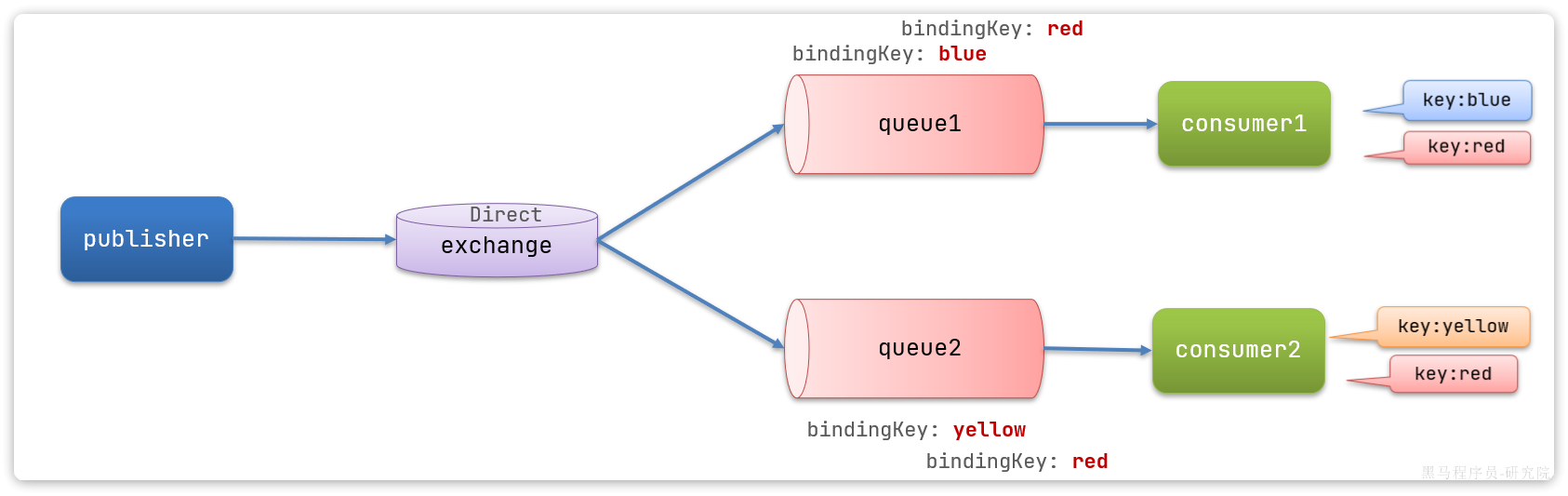
 在Direct模型下:
在Direct模型下:
队列与交换机的绑定,不能是任意绑定了,而是要指定一个
RoutingKey(路由key)消息的发送方在 向 Exchange发送消息时,也必须指定消息的
RoutingKey。Exchange不再把消息交给每一个绑定的队列,而是根据消息的
Routing Key进行判断,只有队列的Routingkey与消息的Routing key完全一致,才会接收到消息
案例需求如图:


声明一个名为
hmall.direct的交换机声明队列
direct.queue1,绑定hmall.direct,bindingKey为blud和red声明队列
direct.queue2,绑定hmall.direct,bindingKey为yellow和red在
consumer服务中,编写两个消费者方法,分别监听direct.queue1和direct.queue2在publisher中编写测试方法,向
hmall.direct发送消息
3.6.1.声明队列和交换机
首先在控制台声明两个队列direct.queue1和direct.queue2。 然后声明一个direct类型的交换机,命名为hmall.direct。 然后使用red和blue作为key,绑定direct.queue1到hmall.direct: 声明过程参考前面
3.6.2.消息接收
在consumer服务的SpringRabbitListener中添加方法:
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct.queue1")
public void listenDirectQueue1(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者1接收到direct.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "direct.queue2")
public void listenDirectQueue2(String msg) {
System.out.println("消费者2接收到direct.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}3.6.3.消息发送
在publisher服务的SpringAmqpTest类中添加测试方法:
@Test
public void testSendDirectExchange() {
// 交换机名称
String exchangeName = "hmall.direct";
// 消息
String message = "红色警报!日本乱排核废水,导致海洋生物变异,惊现哥斯拉!";
// 发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "red", message);
}由于使用的red这个key,所以两个消费者都收到了消息:

 我们再切换为blue这个key:
我们再切换为blue这个key:
@Test
public void testSendDirectExchange() {
// 交换机名称
String exchangeName = "hmall.direct";
// 消息
String message = "最新报道,哥斯拉是居民自治巨型气球,虚惊一场!";
// 发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "blue", message);
}你会发现,只有消费者1收到了消息:

 3.6.4.总结
3.6.4.总结
描述下Direct交换机与Fanout交换机的差异?
Fanout交换机将消息路由给每一个与之绑定的队列
Direct交换机根据RoutingKey判断路由给哪个队列
如果多个队列具有相同的RoutingKey,则与Fanout功能类似
3.7.Topic交换机
3.7.1.说明
Topic类型的Exchange与Direct相比,都是可以根据RoutingKey把消息路由到不同的队列。 只不过Topic类型Exchange可以让队列在绑定BindingKey 的时候使用通配符!
BindingKey 一般都是有一个或多个单词组成,多个单词之间以.分割,例如: item.insert
通配符规则:
#:匹配一个或多个词*:匹配不多不少恰好1个词
举例:
item.#:能够匹配item.spu.insert或者item.spuitem.*:只能匹配item.spu
图示:

 假如此时publisher发送的消息使用的
假如此时publisher发送的消息使用的RoutingKey共有四种:
china.news代表有中国的新闻消息;china.weather代表中国的天气消息;japan.news则代表日本新闻japan.weather代表日本的天气消息;
解释:
topic.queue1:绑定的是china.#,凡是以china.开头的routing key都会被匹配到,包括:china.newschina.weather
topic.queue2:绑定的是#.news,凡是以.news结尾的routing key都会被匹配。包括:china.newsjapan.news
接下来,我们就按照上图所示,来演示一下Topic交换机的用法。 首先,在控制台按照图示例子创建队列、交换机,并利用通配符绑定队列和交换机。此处步骤略。最终结果如下:


3.7.2.消息发送
在publisher服务的SpringAmqpTest类中添加测试方法:
/**
* topicExchange
*/
@Test
public void testSendTopicExchange() {
// 交换机名称
String exchangeName = "hmall.topic";
// 消息
String message = "喜报!孙悟空大战哥斯拉,胜!";
// 发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend(exchangeName, "china.news", message);
}3.7.3.消息接收
在consumer服务的SpringRabbitListener中添加方法:
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.queue1")
public void listenTopicQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者1接收到topic.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(queues = "topic.queue2")
public void listenTopicQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者2接收到topic.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}3.7.4.总结
描述下Direct交换机与Topic交换机的差异?
Topic交换机接收的消息RoutingKey必须是多个单词,以
**.**分割Topic交换机与队列绑定时的bindingKey可以指定通配符
#:代表0个或多个词*:代表1个词
3.8.声明队列和交换机
在之前我们都是基于RabbitMQ控制台来创建队列、交换机。但是在实际开发时,队列和交换机是程序员定义的,将来项目上线,又要交给运维去创建。那么程序员就需要把程序中运行的所有队列和交换机都写下来,交给运维。在这个过程中是很容易出现错误的。 因此推荐的做法是由程序启动时检查队列和交换机是否存在,如果不存在自动创建。
3.8.1.基本API
SpringAMQP提供了一个Queue类,用来创建队列:


SpringAMQP还提供了一个Exchange接口,来表示所有不同类型的交换机:

 我们可以自己创建队列和交换机,不过SpringAMQP还提供了ExchangeBuilder来简化这个过程:
我们可以自己创建队列和交换机,不过SpringAMQP还提供了ExchangeBuilder来简化这个过程:

 而在绑定队列和交换机时,则需要使用BindingBuilder来创建Binding对象:
而在绑定队列和交换机时,则需要使用BindingBuilder来创建Binding对象:


3.8.2.fanout示例
在consumer中创建一个类,声明队列和交换机:
package com.itheima.consumer.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.FanoutExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class FanoutConfig {
/**
* 声明交换机
* @return Fanout类型交换机
*/
@Bean
public FanoutExchange fanoutExchange(){
return new FanoutExchange("hmall.fanout");
}
/**
* 第1个队列
*/
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue1(){
return new Queue("fanout.queue1");
}
/**
* 绑定队列和交换机
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindingQueue1(Queue fanoutQueue1, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue1).to(fanoutExchange);
}
/**
* 第2个队列
*/
@Bean
public Queue fanoutQueue2(){
return new Queue("fanout.queue2");
}
/**
* 绑定队列和交换机
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindingQueue2(Queue fanoutQueue2, FanoutExchange fanoutExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind(fanoutQueue2).to(fanoutExchange);
}
}3.8.2.direct示例
direct模式由于要绑定多个KEY,会非常麻烦,每一个Key都要编写一个binding:
package com.itheima.consumer.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.*;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class DirectConfig {
/**
* 声明交换机
* @return Direct类型交换机
*/
@Bean
public DirectExchange directExchange(){
return ExchangeBuilder.directExchange("hmall.direct").build();
}
/**
* 第1个队列
*/
@Bean
public Queue directQueue1(){
return new Queue("direct.queue1");
}
/**
* 绑定队列和交换机
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindingQueue1WithRed(Queue directQueue1, DirectExchange directExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue1).to(directExchange).with("red");
}
/**
* 绑定队列和交换机
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindingQueue1WithBlue(Queue directQueue1, DirectExchange directExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue1).to(directExchange).with("blue");
}
/**
* 第2个队列
*/
@Bean
public Queue directQueue2(){
return new Queue("direct.queue2");
}
/**
* 绑定队列和交换机
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindingQueue2WithRed(Queue directQueue2, DirectExchange directExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue2).to(directExchange).with("red");
}
/**
* 绑定队列和交换机
*/
@Bean
public Binding bindingQueue2WithYellow(Queue directQueue2, DirectExchange directExchange){
return BindingBuilder.bind(directQueue2).to(directExchange).with("yellow");
}
}
3.8.4.基于注解声明
基于@Bean的方式声明队列和交换机比较麻烦,Spring还提供了基于注解方式来声明。
例如,我们同样声明Direct模式的交换机和队列:
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "hmall.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red", "blue"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者1接收到direct.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "direct.queue2"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "hmall.direct", type = ExchangeTypes.DIRECT),
key = {"red", "yellow"}
))
public void listenDirectQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者2接收到direct.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}是不是简单多了。 再试试Topic模式:
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue1"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "hmall.topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = "china.#"
))
public void listenTopicQueue1(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者1接收到topic.queue1的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
@RabbitListener(bindings = @QueueBinding(
value = @Queue(name = "topic.queue2"),
exchange = @Exchange(name = "hmall.topic", type = ExchangeTypes.TOPIC),
key = "#.news"
))
public void listenTopicQueue2(String msg){
System.out.println("消费者2接收到topic.queue2的消息:【" + msg + "】");
}3.9.消息转换器
Spring的消息发送代码接收的消息体是一个Object:

 而在数据传输时,它会把你发送的消息序列化为字节发送给MQ,接收消息的时候,还会把字节反序列化为Java对象。 只不过,默认情况下Spring采用的序列化方式是JDK序列化。众所周知,JDK序列化存在下列问题:
而在数据传输时,它会把你发送的消息序列化为字节发送给MQ,接收消息的时候,还会把字节反序列化为Java对象。 只不过,默认情况下Spring采用的序列化方式是JDK序列化。众所周知,JDK序列化存在下列问题:
数据体积过大
有安全漏洞
可读性差
我们来测试一下。
3.9.1.测试默认转换器
1)创建测试队列 首先,我们在consumer服务中声明一个新的配置类,利用@Bean的方式创建一个队列,具体代码:
package com.itheima.consumer.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class MessageConfig {
@Bean
public Queue objectQueue() {
return new Queue("object.queue");
}
}注意,这里我们先不要给这个队列添加消费者,我们要查看消息体的格式。
重启consumer服务以后,该队列就会被自动创建出来了:


2)发送消息 我们在publisher模块的SpringAmqpTest中新增一个消息发送的代码,发送一个Map对象:
@Test
public void testSendMap() throws InterruptedException {
// 准备消息
Map<String,Object> msg = new HashMap<>();
msg.put("name", "柳岩");
msg.put("age", 21);
// 发送消息
rabbitTemplate.convertAndSend("object.queue", msg);
}发送消息后查看控制台:

 可以看到消息格式非常不友好。
可以看到消息格式非常不友好。
3.9.2.配置JSON转换器
显然,JDK序列化方式并不合适。我们希望消息体的体积更小、可读性更高,因此可以使用JSON方式来做序列化和反序列化。
在publisher和consumer两个服务中都引入依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.dataformat</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-dataformat-xml</artifactId>
<version>2.9.10</version>
</dependency>注意,如果项目中引入了spring-boot-starter-web依赖,则无需再次引入Jackson依赖。
配置消息转换器,在publisher和consumer两个服务的启动类中添加一个Bean即可:
@Bean
public MessageConverter messageConverter(){
// 1.定义消息转换器
Jackson2JsonMessageConverter jackson2JsonMessageConverter = new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
// 2.配置自动创建消息id,用于识别不同消息,也可以在业务中基于ID判断是否是重复消息
jackson2JsonMessageConverter.setCreateMessageIds(true);
return jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
}消息转换器中添加的messageId可以便于我们将来做幂等性判断。
此时,我们到MQ控制台删除object.queue中的旧的消息。然后再次执行刚才的消息发送的代码,到MQ的控制台查看消息结构:


3.9.3.消费者接收Object
我们在consumer服务中定义一个新的消费者,publisher是用Map发送,那么消费者也一定要用Map接收,格式如下:
@RabbitListener(queues = "object.queue")
public void listenSimpleQueueMessage(Map<String, Object> msg) throws InterruptedException {
System.out.println("消费者接收到object.queue消息:【" + msg + "】");
}
